Introduction
In topics like this, it is important to first define the keywords to pave the way for easy understanding to the reader. In light of this, what does DEFI stand for? And What are Oracles in relation to cryptocurrency? DEFI is the short form of "Decentralized Finance " It refers to a blockchain-based form of finance that is not reliant upon central financial intermediaries such as brokerages or banks to offer traditional financial services. Still, instead, it utilizes smart contracts on blockchains. So instead of having banks as the go-between, the blockchain system is used. You should know that Bitcoin and Ethereum are the first DEFI systems created before others swooped in.
On the other hand, an Oracle is simply the link between a blockchain or smart contract and external data. It is how information can be passed to and fro a smart contract and other data. You know, blockchain can't have access to information or data that is not within its network, so DEFI Oracles are established to close that gap. Many DEFI systems aim to provide low volatility of their cryptocurrency by using their crypto as collateral with some assets in the real world. Due to this, price oracle is a vital component bridging the gap with the external information about the crypto assets' intended value.
Types of Defi Oracle
There are several DEFI Oracles, but based on relevance and functionality, we have selected our top twelve: MakerDAO, Token Sets, Compound, Aave, Augur, Contribute Synthetix, DDEX, bZx, dYdX, Nexus Mutual, and Nuo. These Oracles have their own special contract address. As of now, there are five highly recognized Oracle designs, and we shall delve into each of them briefly.
Distributed
Distributed DEFI oracles function by whitelisting data providers to feed real-world information to the blockchain. It is not a single entity. This is why people can transform the data obtained through averaging methods before executing smart contracts. However, a new approach is known as the 'Relaying Mechanism' is one of the variations that has been introduced as an improvement to the distributed oracle design. It is a hierarchy-like structure where several interested individuals sign on the prices and push the final decision to a higher signatory. The problem with this approach is that it can be easily and quickly manipulated along the relay chain. You can refer to the distributed design as an advanced version of the centralized design, which we will discuss next.
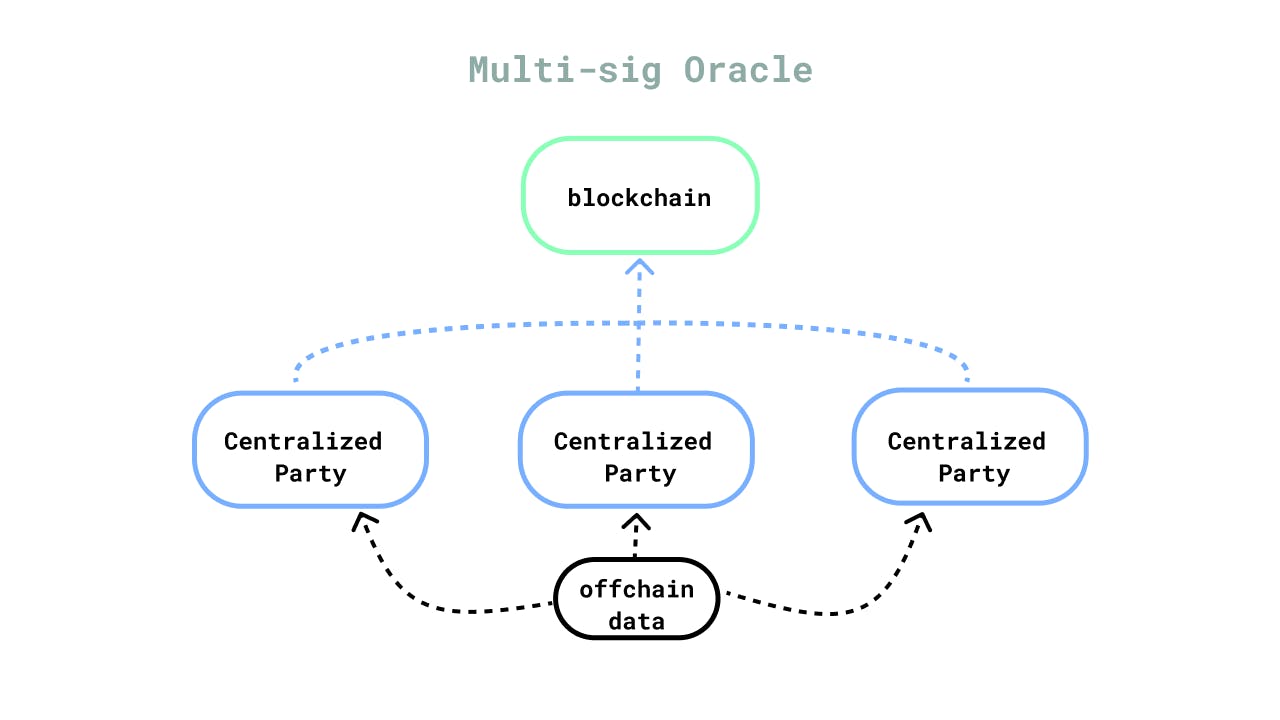
Centralized
This oracle design feeds smart contracts with data based on a central point of information. They are provided by whitelisted entities, which could be the Defi protocol or a 3rd party. Most of the time, these entities include spot and derivatives exchanges such as Drixx. This design is the best in terms of responsiveness because its centralized nature makes them super-fast. However, this speed does not translate to efficiency or reliability as they depend on high levels of trust for them to be reliable. The reason for this is that a whitelisted off-chain data provider can manipulate the data that they feed to on-chain smart contracts. Because of this, the smart contract will not operate in a decentralized manner, thereby defeating the whole purpose of Defi. Centralized oracle designs also have a low degree of liveness, meaning that the external data provider can decide to switch off their resources at any time. And if they do, smart contracts linked to this whitelisted entity would lose connection with real-world data, and no events will be triggered.
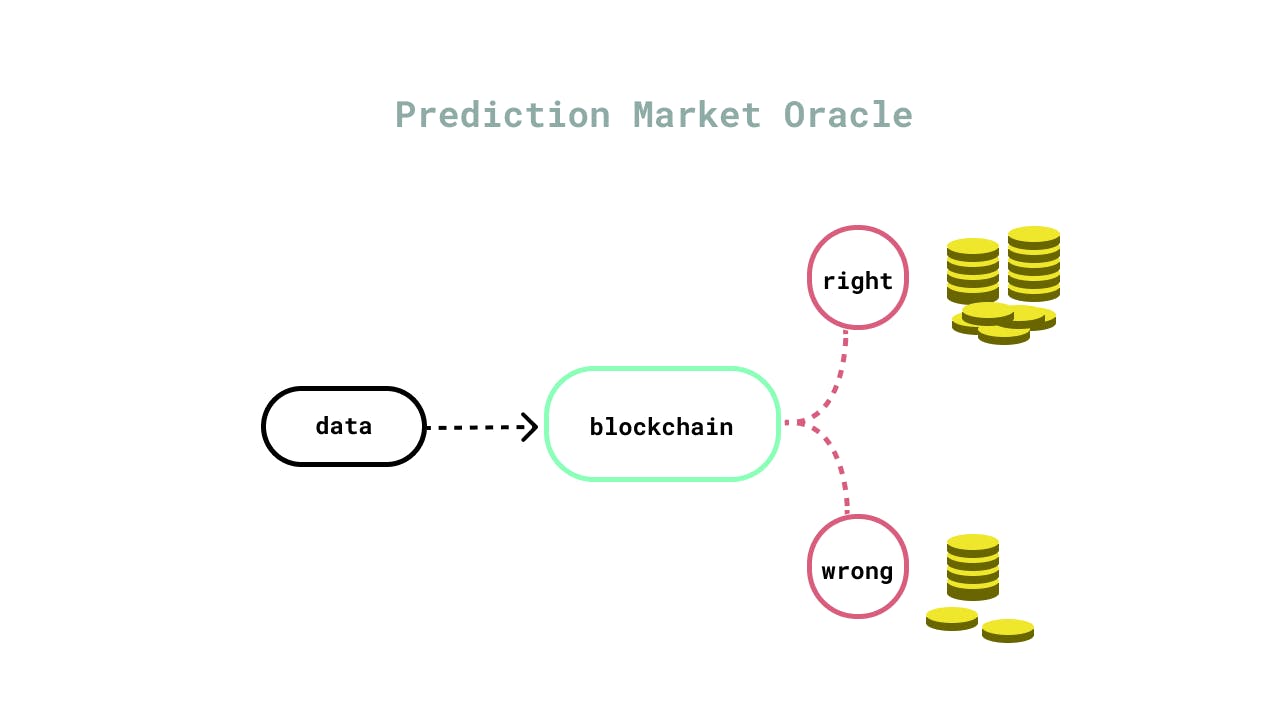
Prediction Market
The prediction market oracle design takes the form of a betting approach to decide on data credibility. In other words, the design is not sure of the authenticity of the data, so it gambles to make its pick. Later on, these bets are decentralized and might even be used as authentic data points to be shared on-chain. The benefits of this oracle design include their resilience and resistance to manipulation, high degree of liveliness, and participation. However, they have regulatory uncertainty, liquidity, and low speed as their downside, but this does not stop developers from using the design.
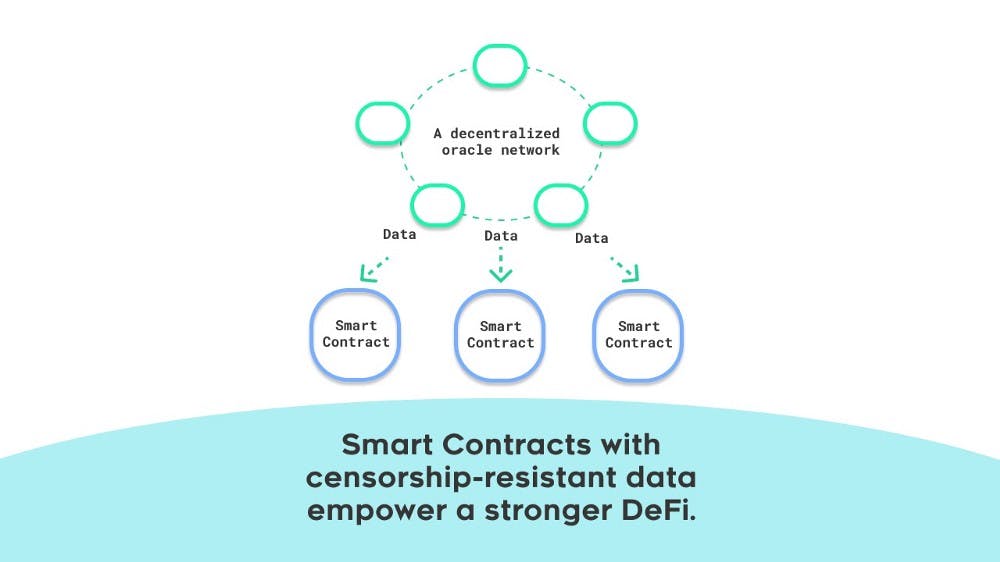
Decentralized
Decentralized oracle designs depend on an open-source network so they can provide off-chain data for smart contract execution. The open-source network is made up of data providers who have agreed on the off-chain data credibility. All their decisions are made using game theory fundamentals and blockchain economic incentives. The aim of this is to attract more data providers to increase the decentralization aspect. Because of how dependent they are on several external data sources, the decentralized designs are more credible than the centralized oracles. Basically, from the perspective of long-term reliability, they have a higher degree of liveness. You can try, but it won't be easy to compromise decentralized oracles since the open-source data providers carry out their operations independently and credibility decisions are unanimous. Again, decentralized oracles, like any other design, have their own issues, such as being quite slow and expensive. Sourcing of data from several external providers is a costly venture compared to a whitelisted central entity. Finally, it takes way more time for the data providers of the design to decide on the credibility (A process that you will do almost seamlessly if you are using centralized Oracle designs).
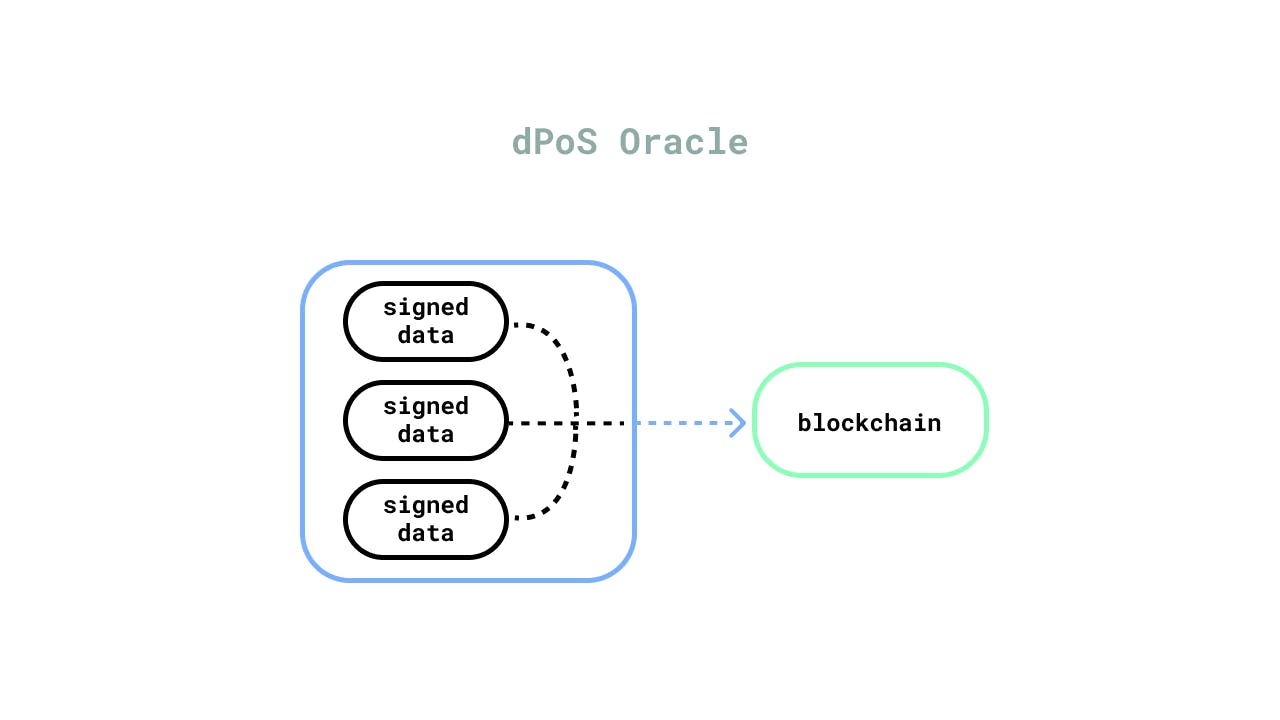
Delegated Proof-of-Stake
For this oracle design, off-chain data is produced from whitelisted staked nodes (Many developers regard this as a better option than the distributed design). Basically, these whitelisted data providers are given staking incentives to provide accurate data, failure of which would result in losing their stake. This is the main basis on which the DPoS oracle model is pegged. The data providers of this design receive the most economic incentives out of all other designs, but this does not mean that all of them act in good faith. Suppose you are a smart contract innovator on the lookout for external DPoS data feeds. In that case, you should better devote a lot of your time to study the fine print on issues such as the supporting entity and whitelisting process. It is also of vital importance to your cause that you get a proper understanding of how nodes operate and the possible risks they can be exposed to.
What does the future hold for DEFI Oracles?
Even though it has served well since its inception, it has also got its issues, but the next step developers are planning will shake the crypto world. They are planning the Adoption of DEFIS Mainstream amongst several other things that have not been revealed to make sure things are easier on all fronts. In conclusion, much has been said to enlighten you about the importance of DEFI Oracles, but this is just the tip of the iceberg. More unique and informative content is to be shared on this platform for your benefit, so refer your friends and family who want to learn about crypto as they are in for a long ride.